How To Setup Cross Domain Tracking GA4

by Olivia Pasfield
With the rollout of Universal Analytics around the corner, it is imperative to ensure you have set up conversion tracking correctly within your Google Analytics 4 property. Whilst most events are relatively easy to set up within GA4, if you find yourself in a situation where you need to track conversions across multiple domains then you'll need to setup cross domain tracking.
If you have previously set up cross domain tracking within Universal Analytics, you will no doubt know that it is a complex configuration that requires either coding on the website or access to Google Tag Manager and even then, it's not full-proof. There are also multiple steps that you need to take when setting up cross domain tracking for Universal Analytics, such as setting up a referral exclusion list and completing the auto link domains field under the Google Analytics settings variable.
However, one benefit of Google Analytics 4 is that the cross domain tracking setup has been incredibly simplified. Meaning you can track multiple domains with just a few simple steps without the need for third-party apps such as Google Tag manager.
This article will show you how to implement cross domain tracking with Google Analytics 4, as well as how to ensure that you have setup cross domain tracking correctly.
Why do you need cross domain tracking?
Firstly, let's talk about the benefits of cross domain tracking and why you would need to implement cross domain tracking. When a user lands on your website, Google Analytics uses first-party cookies to store a ga cookie in the user's browser to track what actions they take on the website, even when going to different pages of the website. However, by default, if a user navigates from domain A to domain B Google Analytics will drop the ga cookie and won't track any further actions the user takes.
Therefore, when a user navigates to the destination domain, Google Analytics will automatically create a new _ga cookie for the same user, meaning they will be tracked as separate users and sessions.
This is where cross domain tracking comes into play. By implementing cross domain tracking, Google Analytics will be able to carry the _ga cookie in the user's browser from the first domain to the destination domain, meaning the same session will be tracked across the separate domains.
It's important to note that you don't need to configure cross domain tracking for subdomain tracking. If you are looking to track subdomains that are linked to the same domain, you just need to set up conversion tracking as usual. Cross domain tracking is only used to track events that occur across separate domains.
How to setup cross domain tracking in Google Analytics 4
Before we get into how to setup cross domain tracking, it's important to note that for cross domain tracking to work correctly, both domains need to have the same Google Analytics property installed. You can install the Google Analytics tracking code directly onto your website or through Google Tag manager.
First, go to the admin section of Google Analytics 4.
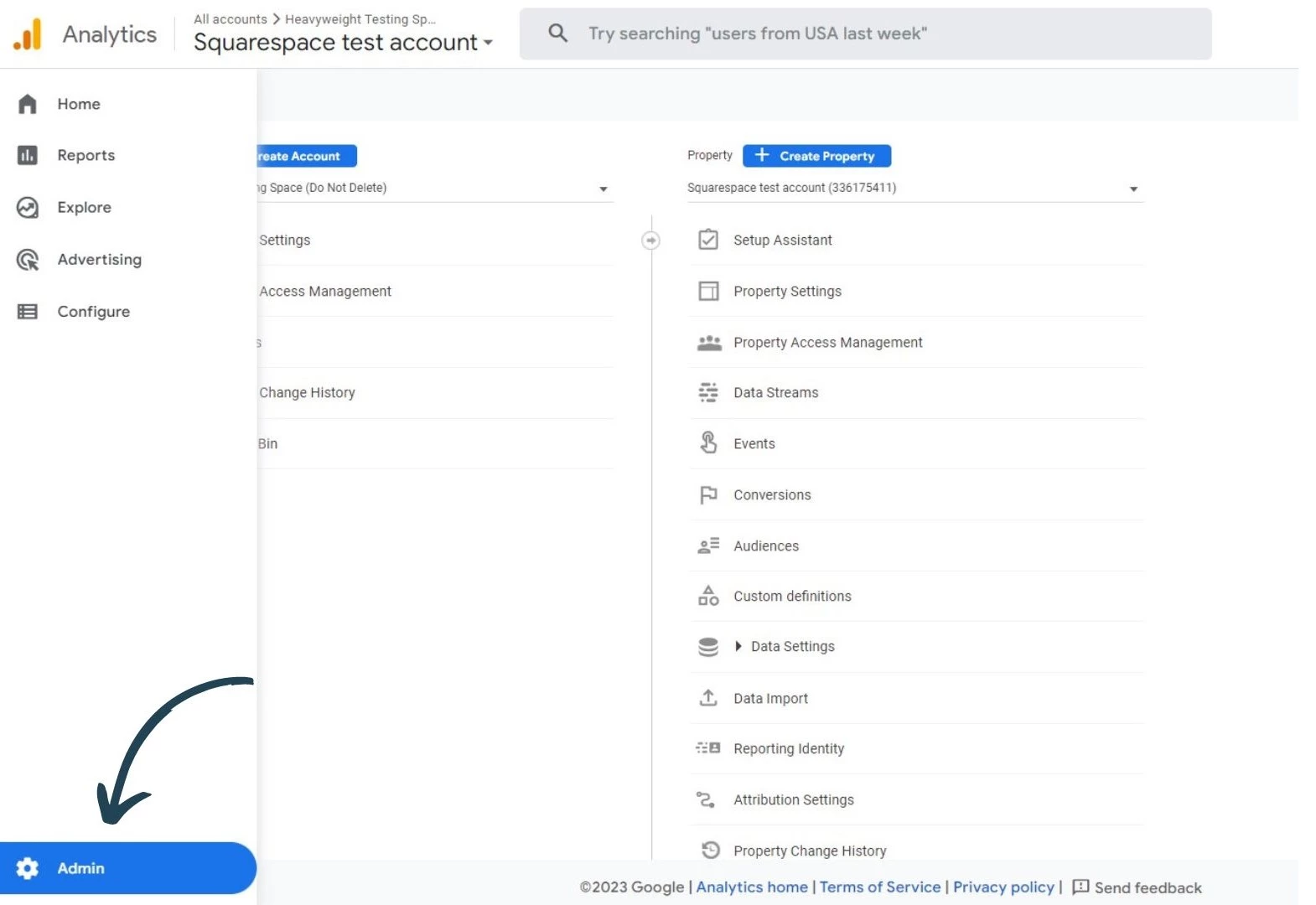
In Admin, go to Data Streams and select the web data stream that you want to setup cross domain tracking for.
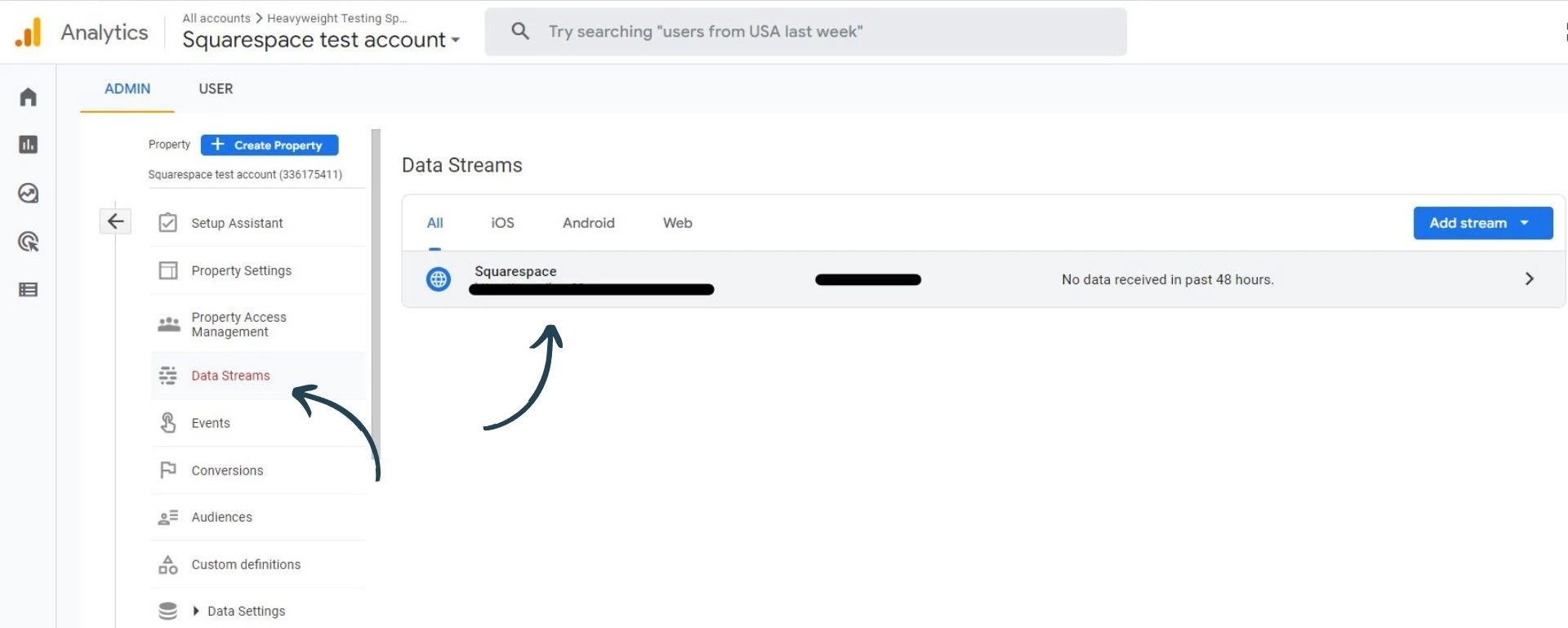
Once you have selected the web data stream, go to configure tag settings under Google tag.
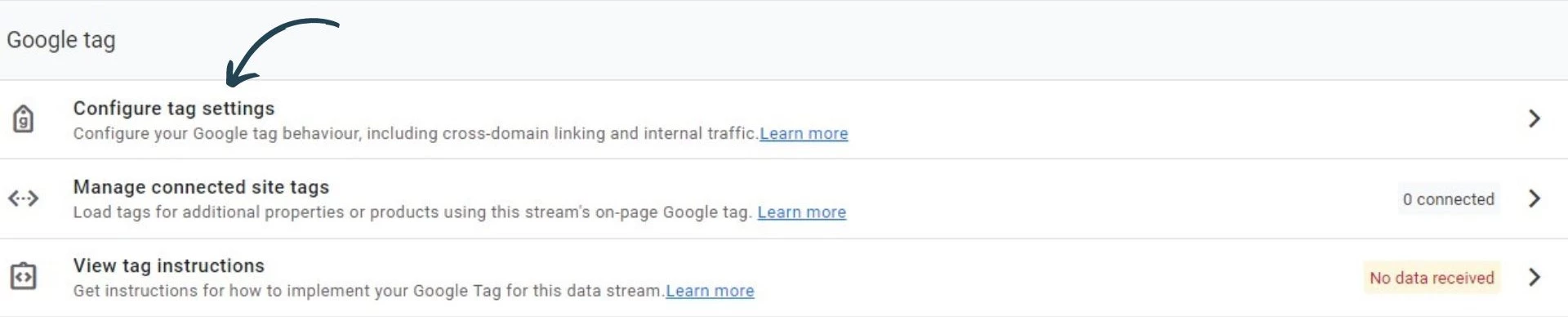
After that, go to configure your domains.
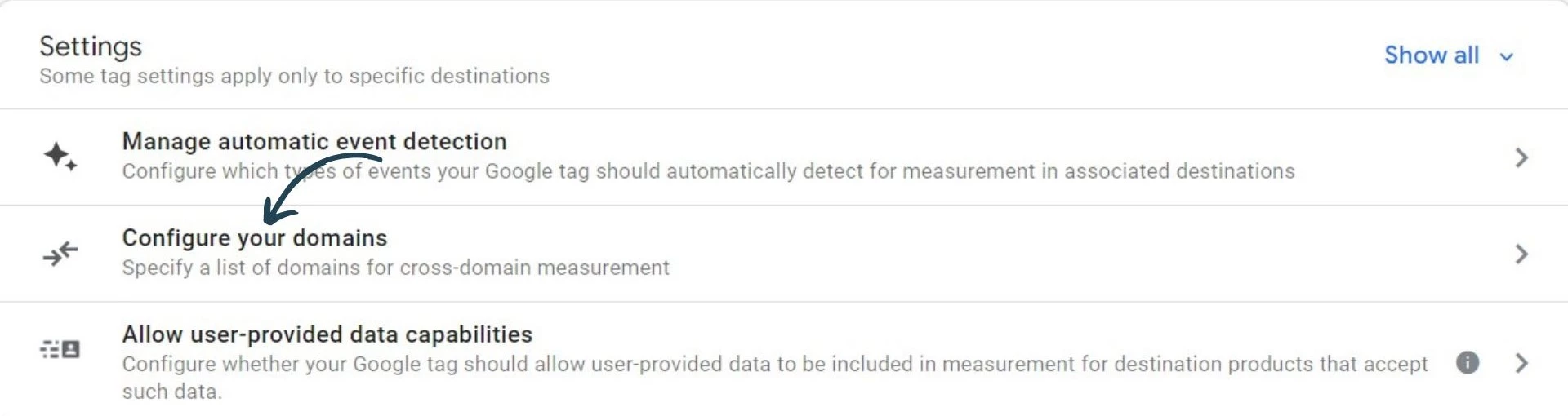
Now, you can enter the domains that you want to include in your cross domain tracking setup and click save.
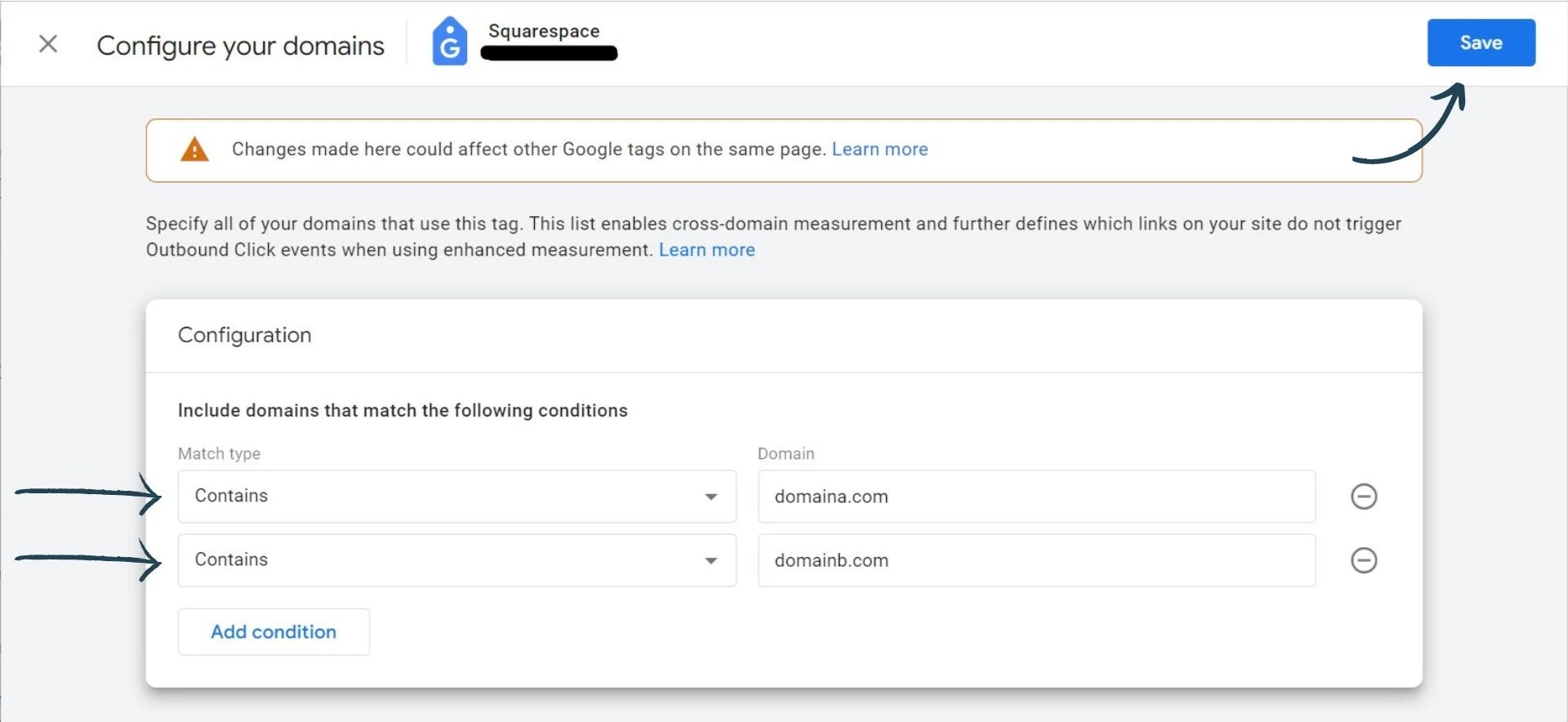
That's it, you have set up cross domain tracking. Unlike Google Analytics UA, you don't need to configure a referral exclusion list as Google Analytics 4 will do this for you.
Test your cross domain tracking setup
Now that you have set up cross domain tracking, you will need to test it to ensure that it works correctly. To test your cross domain tracking setup, go to your first domain (domain A) and find a link that will redirect the user to domain B.
Click on the link so that you get redirected to domain B. Once you are on domain B, check that the URL has a ga cookie. It will look similar to this: ga=2.199638510.1598689227.1674833933-653279331.1665756320
Another way you can test your cross domain tracking setup is by going into the real-time report within Google Analytics 4. First, go to domain A and make sure you are registered as a user within the report, then click the link to redirect you to domain B. You should still see that you are a registered user. You can then click on other pages within domain B and ensure that they are showing within the view by page title report within the Google Analytics real-time report.
Conclusion
Cross domain tracking is a great tool to use when tracking multiple domains and Google Analytics 4 makes it easier to set up cross domain tracking. You no longer have to rely on Google Tag Manager to assist you with the setup by enabling AllowLinker or auto link domains.
With Google Analytics 4's simplified configuration, anyone can set up cross domain tracking in just a few simple steps.